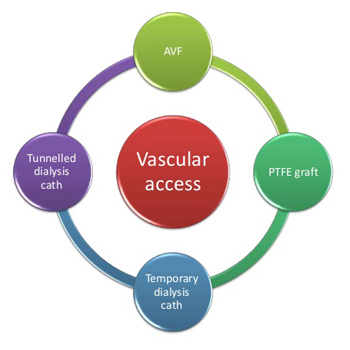
The vascular access will allow the blood of the patient to leave the body and be brought to the artificial kidney or dialyzer to be cleaned or filtered.The three most common types of vascular access for hemodialysis are central venous catheters, native arteriovenous (AV) fistulas and synthetic grafts
Catheters are flexible, hollow tubes with two lumens. Blood leaves the patient’s body passing through one lumen, enters the dialysis circuit, and is returned to the body via the other lumen.Two types of venous catheters are available, tunnelledand non-tunnelled.
The arteriovenous or AV fistula is the most common and the best method of vascular access for long term hemodialysis.
An arteriovenous graft is another form of long term dialysis access, which can be used when persons do not have satisfactory veins for an AV fistula or have a failed AV fistula.
